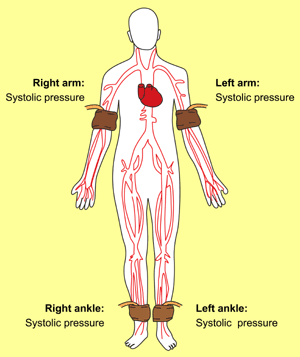
Figure 1: Measurement of the ankle-brachial index (ABI).
| Systolic blood
pressure is measured by Doppler ultrasonography in each arm and in
the dorsalis pedis (DP) or posterior tibial (PT) arteries in each
ankle. The higher of the two brachial arm pressures is selected if
the difference is |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||