| ACE inhibitors |
| Heart failure |
| Left ventricular dysfunction post-myocardial infarction
or established coronary heart disease |
| Type 1 diabetic nephropathy |
| Secondary stroke prevention |
|
| Chronic renal disease |
| Type 2 diabetic nephropathy |
| Proteinuria renal disease |
|
| Renal impairment |
| Peripheral vascular disease |
|
| Pregnancy |
| Renovascular disease |
|
| Angiotensin II receptor blockers |
| Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor intolerance |
| Type 2 diabetic nephropathy |
| Hypertension with left ventricular hypertrophy |
| Heart failure in angiotensin converting enzyma intolerant
patients, after myocardial infarction |
|
| Left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction |
| Intolerance of other antihypertensive drugs |
| Proteinuria renal disease, chronic renal disease
|
| Heart failure |
|
| Renal impairment |
| Peripheral vascular disease |
|
| Pregnancy |
| Renovascular disease |
|
| Calcium channel blockers (dihydropyridine) |
| Elderly patient isolated systolic hypertension |
|
|
|
|
| Calcium channel blockers (rate limiting) |
|
|
Combination with 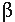 blockade
blockade |
|
| Heart block, heart failure |
|
| Thiazides or thiazide-like diuretics |
| Elderly patient, isolated systolic hypertion, heart
failure, secondary stroke prevention |
|
|
|
|
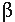 Blockers Blockers |
| Myocardial infarction, angina |
|
|
| Heart failure |
| Peripheral vascular disease |
| Diabetes (except with coronary heart disease) |
|
| Asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| Heart block |
|
 Blockers Blockers |
| Benign prostatic hypertrophy |
|
|
| Postural hypotension, heart failure |
|
|