Summary
Objective: To establish the psychometric properties and
norm of the Chinese (HK) SF-36_ version 2 Health Survey
for the adult population in Hong Kong (HK) to facilitate
its application and interpretation.
Design: A cross-sectional random telephone survey of
the general adult population.
Subjects: 2410 Chinese adults randomly selected from
the general Chinese adult population in Hong Kong. The
mean age of the subjects was 42.9 (S.D. 17.3) years, 48%
were men and 38% had one or more chronic disease.
Main outcome measures: Responses to the SF-36v2
Health Survey questions were extracted. Item-scale
correlations, internal and test-retest reliabilities, and the
factor structure of the SF-36v2 Health Survey scores were
analysed. The SF-36v2 Health Survey scores were
calculated by the standard algorithm to establish the
population norm.
Results: All items had 100% scaling success indicating
discriminant validity. Internal consistency and test-retest
reliabilities of all scales were good (coefficients 0.66 to
0.89). The hypothesized two-factor structure underlying
construction of the physical and mental health summary
scales was confirmed. The psychometric properties of
the SF-36v2 Health Survey were generally better than
version 1. There were significant differences in the
population norms between versions 1 and 2 of the
Chinese (HK) SF-36 Health Survey, especially in the rolephysical
and role-emotional scales.
Conclusion: The Chinese (HK) SF-36v2 Health Survey is
valid and reliable for measuring HRQOL of Chinese adults
in Hong Kong, and population norm is now available to
support the interpretation of its scores.
Keywords: Quality of life, SF-36, Norm, Chinese, validity,
reliability, psychometrics
摘要
目的:確定中國人(香港)SF-36第二版的健康調查的精神測定
特性和標準適用於香港成年人口,以方便其應用和解釋。
設計:橫切面的隨機抽樣電話調查,目標是普羅成年人。
對象:從普羅的香港中國成年人口隨機抽樣抽出2410人。平
均年齡為42.9(S.D.17.3)歲, 48% 為男性, 38% 有一樣和超
個一樣的慢性病。
主要測量內容:SF-36v2健康調查結果全收集起來。項目/標
度相關,內部和重複測試可靠性,和SF-36v2成份結構分析。
然後用標準的方程式去計算SF-36v2健康調查的分樓來算出人
口的特性和標準。
結果:所有項目均達到100% 定標成功,標示出辨別的可靠
性。內部協合和重複測試可靠性都非常好( 系數為0 . 6 6
至0.89) 。雙份子結構的假設在其基本結構,生理和心理健
康,標分受到確定。SF-36v2 的表現比SF-36v1 為佳。SF-
36v2 和SF-36v1 的人口特性有很明顯分別,尤其是在心理功
用和生理功用標度方面。
結論:中文(香港)SF-36v2健康調查是可靠和可信的,可準確
量度香港成年人口的生活質素。現在我們已找出其人口特性來
支持其分數的解釋。
主要詞彙:生活質素, SF-36 ,特性,中文,可信性,可靠
性,精神測定
Introduction
The SF-36 Health Survey developed by Ware et al.
is the most widely used health-related quality of life
(HRQOL) measure in Hong Kong (HK) and worldwide.1-3
The survey includes 35 items measurement HRQOL that
are summarized into eight multi-item scales, along with 1 item on health change. The first version of the SF-36
Health Survey (version 1) has been adapted and validated
in more than 40 populations with norm references
available from 14 populations including Hong Kong.3, 4
Several weaknesses of version 1 were identified: the
layout of the questions was inconsistent, colloquial or
double negative wordings were used, psychometric
performance of the role-physical (RP) and role-emotional
(RE) scales (questions 4 and 5, respectively) was
suboptimal due to the use of dichotomous (yes/no)
responses; and the differentiation between some of the six
response options of question 9 may be difficult for some
respondents.5-7 Modification to the SF-36 Health Survey
was carried out by the original authors to address these
problems and version 2.0 (SF-36v2 Health Survey) was
produced in 1996.4
The changes included reformatting the layout of the
questions and answers to a consistent horizontal format,
revision of some wordings of questions 3, 4, 5 and 9;
replacement of the dichotomous response choices with a
5-point frequency scale for the items of questions 4 and
5; and deleting the response option ‘a good bit of the time’
from question 9 to change the 6-point to a 5-point scale.
Most of the changes in the wordings had already been
incorporated into the Chinese (HK) SF-36 Health Survey
during the version 1 translation process, and the Chinese
translations for all the statements and response options
included in the SF-36v2 Health Survey could be extracted
from version 1, so repeat translation was not necessary.
The differences between the two versions of the Chinese
(HK) SF-36 Health Survey are shown in the Appendix.
Studies in the United States, United Kingdom,
Sweden and Australia have confirmed that SF-36v2 Health
Survey was superior to version 1 in that it had fewer
missing data, lower floor and ceiling effects, better score
precision and a higher sensitivity for the role functioning
scales.4, 8-11 Version 2 is expected to replace version 1 of
the SF-36 in the near future. We need to establish the
psychometric properties and norm of the SF-36v2 Health
Survey before it can be applied and interpreted properly
in our Hong Kong population.
In the population validation and norming study of the
Chinese (HK) SF-36 Health Survey in Hong Kong the two
role-functioning questions that were modified for version
2 were also included, providing an opportunity for the
extraction of population data on the SF-36v2 Health
Survey. The aim of this study was to determine the psychometric properties and population norm of the
Chinese (HK) SF-36v2 Health Survey.
Methods
Sample
2410 Chinese adults randomly selected from the
general Chinese adult population in HK were interviewed
by telephone. The response rate of this survey was 84.4%
(2410 out of 2857 sampled). The mean age of the subjects
was 42.9 (range 18 to 88, S.D. 17.3) years old, 48% were
men and 38% had one or more chronic disease. The
sociodemographic characteristics of the subjects were
comparable to those found in the population Census. The
details of the sampling and survey methods are described
in earlier papers.3, 12
The first 240 subjects who agreed to a repeat survey
were contacted 2 weeks later to answer the questions
again to determine test-retest reliability and 200 (83%)
completed the retest.
Survey instruments
The survey instruments consisted of the Chinese
(HK) SF-36 Health Survey (version 1), followed by
questions 4 (role-physical items) and 5 (role-emotional
items) of the Chinese (HK) SF-36v2 Health Survey, and
a s truc ture d qu estionnai re o n so cio demo grap hy,
morbidity and service utilization. The instruments were
administered by trained interviewers in Cantonese.
Data analysis
All data analyses were carried out with the SPSS for
Windows 15.0 programme. Statistical significant levels
were set at p values less than 0.05.
The Chinese (HK) SF-36v2 Health Survey data were
extracted from the responses to questions 1, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9,
10 and 11 of version 1, which were the same as those of
version 2, and the responses to the SF-36v2 Health Survey
questions 4 and 5. The response value ‘a good bit of the
time’ for question 9 items was recoded randomly to the
adjoining values of ‘most of the time’ or ‘some of the
time’ for the calculation of the SF-36v2 vitality and
mental health scale scores. Item responses recoding and
scale score calculations were carried out according to the
standard methods described in the SF-36v2 Health Survey
manual.10
The construct validity of the Chinese (HK) SF-36v2
Health Survey scales was tested by item-scale Pearson
correlation to assess whether items:
- were substantially correlated (r ³ 0.4) to the
hypothesized scale score.
- have similar item-scale correlations and equal
variance (standard deviation) in the same scale to
justify summation without weighting.
- correlated significantly higher (greater than two
standard errors) with their hypothesized scale than
other scales. The percentage of this scaling success
on item discriminant validity by the total number of
item-scale correlations of each scale was calculated.
Factor analysis using the varimax rotation method
was done on the scale scores to extract two principal
components and test the hypothesized two-dimensional
(physical and mental) of the SF-36v2 Health Survey. The
two principal components should explain ³ 60% of the
total variance of the SF-36v2 Health Survey scores, and
³ 70% of the reliable variance of each scale score, as
found in the US and other populations.13 The pattern of
correlations between the eight scales and two rotated
components was examined to determine the basis for the
components interpretation as physical and mental
summary measures.
Internal consistency (reliability) of scale scores was
measured by the Cronbach’s alpha coefficient and testretest
reliability was assessed by intra-class correlation
(ICC). The recommended standard is 0.7 or greater for
group comparisons.
Descriptive statistics including mean, standard
deviation (SD), ceiling and floor proportions of the scale
scores of SF-36v2 Health Survey were calculated for the
whole sample and by age-sex groups to be used as the
population norm reference.
Results
Validity and reliability of the scales
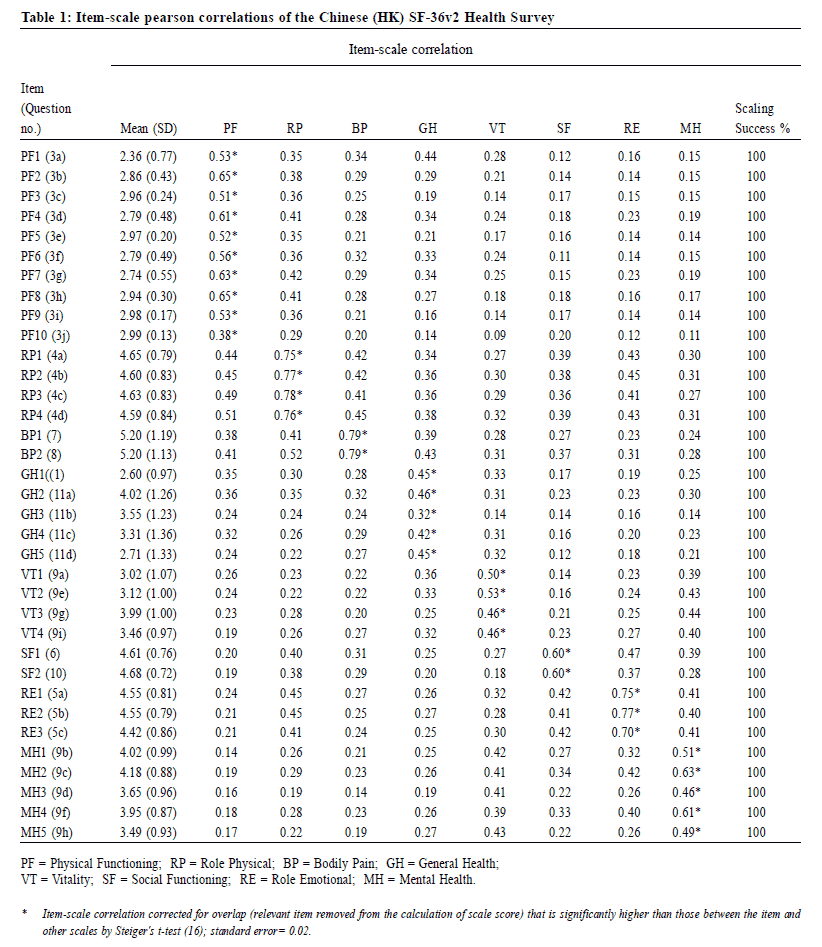
Table 1 shows the item-scale Pearson correlations
between each item and the scales. The correlation
between each item and its hypothesized scale (after
correction for overlap) was >0.4 except for PF10 (0.38)
and GH3 (0.32), supporting item internal consistency. The
item-scale correlations and standard deviations of items of the same scale were similar, supporting equal item
weighting. The item-scale correlations for the SF-36v2
Health Survey RP items (0.75 to 0.78) were generally
greater than those of version 1 (0.64 to 0.68). The same
was also found with the RE items (0.70 to 0.77 for version
2 vs 0.62 to 0.71 for version 1). The item-scale
correlations of the version 2 vitality (VT) and mental
health (MH) items were similar to those of version 1
despite a change from the 6-point to a 5-point response
scale. The item-hypothesized scale correlations were
significantly higher than item-other scales correlations for
a ll i tems , wh ic h me an s sc al in g su cc es s on i tem
discriminant validity was perfect (100%) for all scales.
Cronbach’s alpha coefficients of internal consistency
(reliability) were above 0.7 for all the Chinese (HK)
SF-36v2 Health Survey scales except the general health
(GH) scale (0.66), which was the same for both versions
1 and 2 (Table 2). The reliabilities of the RP and RE
scales of version 2 were better than those of version 1
(0.89 in RP_v2 vs. 0.83 in RP_v1; 0.86 in RE_v2 vs. 0.82
in RE_v1). There was almost no difference in the internal
reliability in the VT and MH scales between version 1 and
2 despite a reduction in the number of response options
in version 2. Intra-class coefficients (ICC) measuring testretest
reliability were above 0.7 for all scales.
Validity of the two principal component factor structure
The results of the factor analysis with varimax
rotation on the Chinese SF-36v2 Health Survey scale
scores are shown in Table 3. Two principal component
factors (physical and mental) with eigenvalues greater
than 1.0 (3.61 for factor 1 and 1.01 for factor 2) were
extracted from the eight scale scores. The two principal
components explained 59% of the total variance of SF-36
scores and 64 to 87% of the reliable variance of each
individual scale. The correlations between the scale
scor es and the two f actors were simi lar to those
hypothesized and to those of version 1.14 The population
specific factor coefficients of the Chinese (HK) SF-36v2
Health Survey are compared with those of version 1 with
reference to the US standard in Table 4.

Population norm of the Chinese (HK) SF-36v2 Health
Survey
Table 5 shows the distribution of Chinese (HK)
SF-36v2 Health Survey scale scores, compared with
corresponding values of version 1 as appropriate. The
scores of the PF, BP, GH, SF scales were the same for version 1 and 2 because there was no difference in their
items or response options. There were significant
differences in the mean and SD of the RP and RE scale
scores between the two versions. The floor effect (the
proportion of respondents scoring at the lowest scores) was markedly reduced from 7.5% in version 1 to 0.6% in
version 2 and from 16.4% in version 1 to 0.3% in version
2 for the RP and RE scales, respectively. There was slight
improvement in the ceiling effects (the proportion of
respondents scoring at the highest scores) in these two role functioning scales in version 2, but they were still
very large. Table 6 shows the population mean Chinese
(HK) SF-36v2 Health Survey scores of all subjects and
by age and sex groups.


Discussion
The results confirmed that the Chinese (HK) SF-36v2
Health Survey satisfied all the scaling assumptions with
a scaling success rate of 100%. The correlation between item GH3 and the GH score was relatively low (0.32),
which was the same with both versions. Feedback from
the interviewers revealed that some respondents said that
they were not sure of the answer to this item because they
did not know the health status of others. This might also
be the reason why the internal reliability of the GH scale
did not reach the standard of 0.7
The psychometric properties of version 2, especially
for the two role functioning (RP and RE) scales, were
much better than those of version 1 in terms of internal re l i ab i l i t y, f lo o r e f f e c t s an d sma l l e r s t an d a r d
deviations, suggesting that it would be more sensitive
and responsive. This illustrated the advantage of a
5-point response scale over that of a dichotomous
scale. The floor effects were almost eliminated by the
change from version 1 to 2, implying that the measure
wo u l d b e mo r e ab l e t o d e t e c t d e t e r i o r a t io n in
HRQOL. The ceiling effects of the SF-36v2 Health
Survey were not much improved from those of version 1, as found in population studies in the US and other
countries.4, 8-10 High ceiling effects in the pain and
ro l e - fu n c t io n in g s c a l e s a r e in t r in s i c to g e n e r a l
population studies because most subjects are healthy.
It is more important for a HRQOL measure to have
low floor effect in the normal population so that it can
detect deterioration from ‘normal’, as in the case of
the SF-36v2 Health Survey. On the other hand, the
ceiling effect should be low in patient populations if the measure is to be used to assess the effectiveness
of treatment. Further studies are required to determine
the ceiling effect of the SF-36v2 Health Survey in patient
populations.
Th e h y p o th e s i z e d two p r in c ip a l c omp o n e n t
factor structure that is the conceptual base of the
SF-36 physical and mental summary (PCS & MCS)
sco res was al so co nfirmed. The two compone nts
explained 59% of the total variance of the Chinese
(HK) SF-36 v 2 He a lth Su rve y s c o re s , wh ic h was
slightly better than the 58% found in version 1,14 and
approaching the expected standard of 60%. The two
components explained 70% or more of the reliable
variance of each scale score except for the BP (64%),
VT (6 9%) and SF (65%) sc al e s, s imi la r to th os e
found with version 1.14 The replication of the two
principal factor structure means that summation of
th e Ch ine s e (HK) SF-3 6v 2 He a l th Su rve y s c a l e
scores into the physical and mental summary scores
is valid. The physical and mental factor coefficients
(weightings for the calculation of the SF-36 physical
and mental summary scores) were almost the same be twe en v ers ion s 1 and 2, an d compa rab le to the
s t a n d a r d d e r i v e d f r om t h e U S p o p u l a t i o n .
Eq uiv ale nce b etween th e p opu lat ion s pec ifi c and
standard (US) summary scale scoring algorithms of
Chinese (HK) SF-36 Health Survey was confirmed
in a p r e v io u s s tu d y. 14 Th u s th e Ch i n e s e (HK)
S F - 3 6 v 2 He a l t h S u r v e y p h y s i c a l an d me n t a l
summary (PCS and MCS) scales should be scored by
th e s t an d a r d a lg o r i thm fo r b e t t e r in t e rn a t i o n a l
comparability.
T h e r e wa s s i g n i f i c an t d i f f e r e n c e i n t h e
population mean RP and RE scale sc ores between
version 1 and version 2 indicating th at normative
v a l u e s o f v e r s i o n 1 c an n o t b e u s e d f o r t h e
i n t e r p r e t a t i o n o f v e r s i o n 2 d a t a . Th e t o t a l
p o p u la t io n me an s c o r e s an d s t an da rd d e v iat io n s
shown in Table 6 shou ld be used for norm-based
s c o r i n g o f t h e Ch i n e s e (HK) S F - 3 6 v 2 He a l t h
Survey.14, 15 We believe the normative scores are still
applicable although the data were collected nearly 10
years ago, based on the findings by studies in the US
showing that population mean SF-36 Health Survey
scores remained very stable with a change of less
than 3% (3 points in a scale range of 100) over 10
years.15
Limitation
The Chinese (HK) SF-36v2 Health Survey data
presented in this paper were extracted from answers
to relevant version 1 questions and the two SF-36v2
Health Survey role-functioning questions that were
administered after version 1 questions, which could
have an order effec t on the res ponses. A g eneral
population survey with a stand-alone SF-36v2 Health
S u r v e y s h o u l d b e c a r r i e d o u t t o c o n f i rm t h e
psychometric properties and update the population
norm if resources are available.
Conclusion
Th e v a l i d i t y an d r e l iab i l i ty o f th e Ch in e s e
(HK) SF-36_Version 2 have been confirmed for the
adult population in Hong Kong. Population norm
(mean and standard deviation) of the Chinese (HK)
SF-36v2 Health Survey is now available to facilitate
the interpretation of scores. There was significant
difference in the population means between versions 1 and 2, the appropriate norm reference should be
used for comparison. Version 2 of the Chinese (HK)
SF-36 Health Survey should be preferred to version
1 i n fu t u r e ap p l i c a t i o n s b e c a u s e i t h a s b e t t e r
p s y c h ome t r i c p r o p e r t i e s . Th e Ch i n e s e (HK)
SF-3 6 v 2 He a l th Su rv e y i s e x p e c t e d to b e mo r e
sensitive and responsive than the original version,
which will need to be confirmed by further studies.
Acknowledgement
T h e S F - 3 6 â an d S F - 3 6 v 2 â a r e r e g i s t e r e d
trademarks of Medical Outcomes Trust. A copy of
t h e Ch i n e s e (HK) S F -3 6 v 2 He a l t h S u r v e y an d
licence to use can be obtained from QualityMetric
http://www.qualitymetric.com.
Key messages
- Version 2 of the SF-36 Health Survey (SF-36v2)
has improvements in the clarity of wording,
questionnaire format and number of response
options over the first version.
- The Chinese (HK) SF-36v2 is valid with 100%
scaling success in convergent and discriminant
validity, and reliable.
- The two principal component factor structure and
coe fficients of the Chinese (HK) SF-36v2 is
equivalent to the US original, so the standard
scoring algorithm for the calculation of the two
summa ry score s is applicable to the Chinese
population.
- The SF-36v2 is likely to be more sensitive than
version 1 because it has less floor effect and a
better internal reliability.
- The appropriate population norms should be used
for the interpretation of the data of version 1 or
2 of the SF-36 Health Survey because there were
significant differences in their population mean
scores.
Funding: This study was funded by Health Services Research Grant (#711026),
the Government of the HKSAR.
Elegance TP Lam, BSc, MMedSc
PhD Candidate,
Cindy LK Lam, MBBS, MD (HK), FRCGP, FHKAM (Family Medicine)
Clinical Professor,
Yvonne YC Lo, MBChB, FRACGP, FHKCFP, FHKAM (Family Medicine)
Clinical Assistant Professor,
Family Medicine Unit, Department of Medicine, the University of Hong Kong.
Barbara Gandek, MS
Scientist,
Health Assessment Lab, Waltham, USA
Correspondence to: Professor Cindy L K Lam, Family Medicine Unit, the
University of Hong Kong, 3/F, Ap Lei Chau Clinic, 161 Main
Street, Ap Lei Chau, Hong Kong SAR.
Reference
- Ware JE Jr., Snow KK, Kosinski M, et al. SF-36 Health Survey - Manual
and Interpretation Guide. Boston: The Health Institute, 1993.
- Lam CLK, Gandek B, Ren XS, et al. Tests of scaling assumptions and
construct validity of the Chinese (HK) version of the SF-36 Health Survey.
J Clin Epidemiol 1998;51:1139-1147.
- Lam CLK, Lauder IJ, Lam TP, et al. Population based norming of the
Chinese (HK) version of the SF-36 health survey. HK Pract 1999;21:460-
470.
- Ware JE Jr. SF-36 Health Survey Update. SPINE 2000;25:3130-3139.
- Bullinger M, Alonso J, Apolone G, et al. Translating health status
questionnaires and evaluating their quality: the IQOLA Project approach.
International Quality of Life Assessment. J Clin Epidemiol 1998;51:913-
923.
- Keller SDWare JE, Gandek B, et al. Testing the equivalence of translations
of widely used response choice labels: Results from the IQOLA Project. J
Clin Epidemiol 1998;51:933-948.
- Wagner AK, Gandek B, Aaronson NK, et al. Cross-cultural comparisons of
the content of SF-36 translations across 10 countries: Results from the IQOLA
Project. J Clin Epidemiol 1998:51:925-932.
- Jenkinson C, Stewart-Brown S, Petersen S, et al. Assessment of the SF-36
version 2 in the United Kingdom. J Epidemiol Community Health 1999;53:
46-50.
- Taft C, Karlsson J, Sullivan M. Performance of the Swedish SF-36 version
2.0. Qual Life Res 2004;13:251-256.
- Ware JE Jr., Kosinski MA, Dewey JE. How to score version 2 of the SF-36
health survey. Lincoln: Quality Metric Inc., 2000.
- Hawthorne G, Osborne RH, Taylor A, et al. The SF36 Version 2: critical
analyses of population weights, scoring algorithms and population norms.
Qual Life Res 2007;16:661-673.
- Lam CLK, Fong DY, Lauder IJ, et al. The effect of health-related quality
of life (HRQOL) on health service utilisation of a Chinese population. Soc
Sci Med 2002;55:1635-1646.
- Ware JE Jr., Kosinski M, Gandek B, et al. The factor structure of the SF-36
Health Survey in 10 countries: results from the IQOLA Project. J Clin
Epidemiol 1998;51:1159-1165.
- Lam CLK, Tse EYY, Gandek B, et al. The SF-36 summary scales were valid,
reliable, and equivalent in a Chinese population. J Clin Epidemiol 2005;58:
815-822.
- Ware JE Jr., Kosinski M. SF-36 Physical & Mental Health Summary Scales:
A Manual for Users of Version 1. Lincoln, Rohode Island: QualityMetric,
2001.
- Steiger JH. Tests for comparing elements of a correlation matrix. Psychol
Bull 1980; 87: 245-251.
Appendix: Summary of Difference between Versions 1 and 2 of the Chinese (HK) SF-36 Health Survey
Question Number
3, introduction
Version 1
The following items are about activities you might do during a typical
day. Does your health now limit you in these activities? If so, how much?
Version 2
The following questions are about activities you might do during a typical
day. Does your health now limit you in these activities? If so,how much?
